Token Metadata
About token metadata and metadata enrichment.
Token metadata is not stored as dataset!
Intro
On Solana, token metadata is critical for understanding and working with tokens, especially fungible tokens, NFTs, and programmatic assets. Metadata includes essential details like token names, symbols, descriptions, and associated assets (e.g., images or files). Unlike on-chain data, metadata is typically stored off-chain, requiring additional steps to access and integrate it with on-chain datasets.
AlphaArc provides tools to work with Solana token metadata by normalizing URLs and facilitating metadata retrieval but does not store metadata as part of its chunked datasets. Instead, metadata processing is designed as a postprocessing step, ensuring flexibility and efficient integration.
How Metadata is Stored on Solana
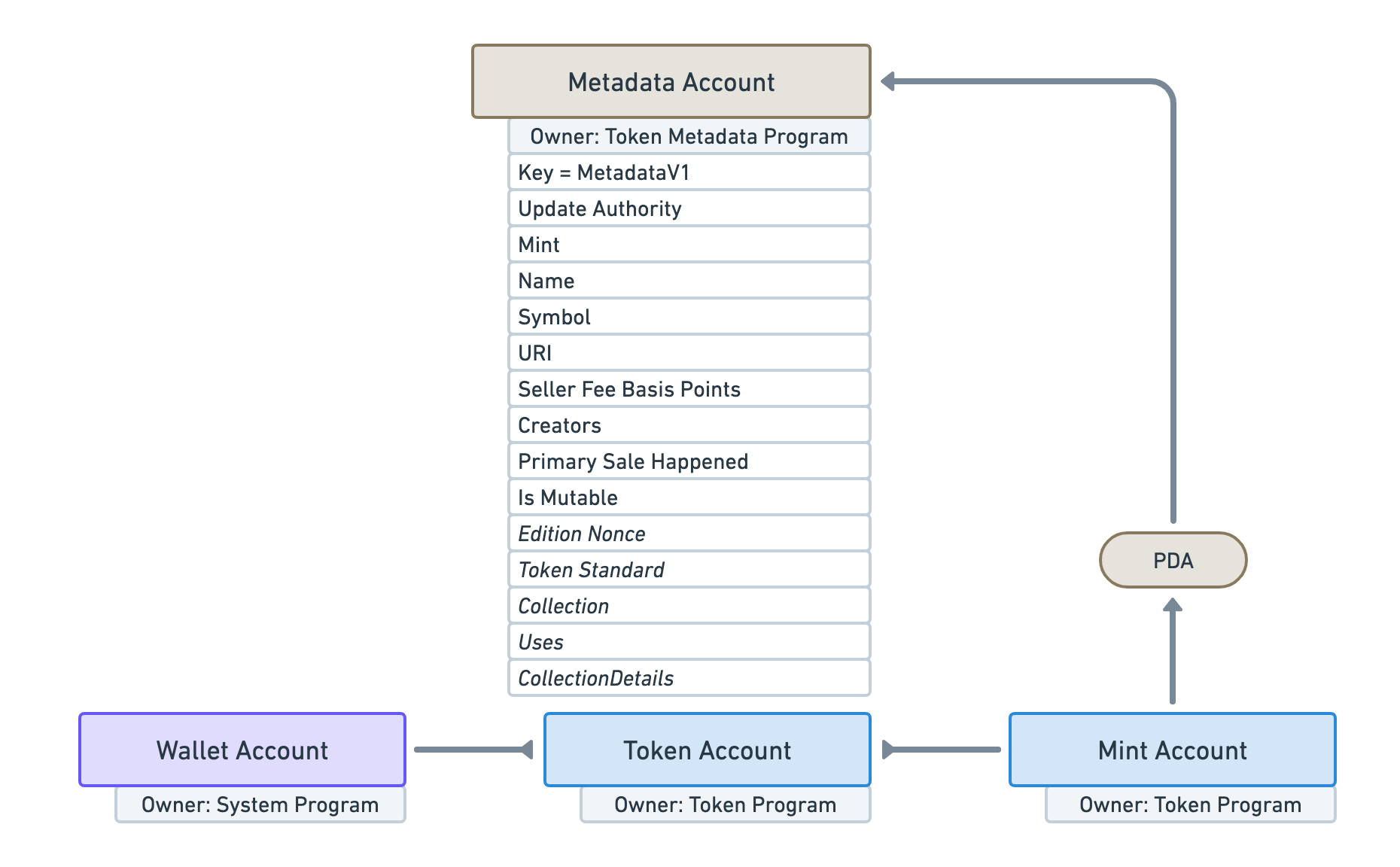
Solana tokens have two types of metadata: on- and off-chain.
Additional metadata is often stored on trackers like Dexscreener.
Token Metadata Program:
- Solana uses the Metaplex Metadata Program to manage metadata for tokens.
- Metadata accounts are linked to tokens via the token's mint address.
- Each metadata account stores a JSON URI pointing to the token's metadata.
 Source: docs.metaplex.com
Source: docs.metaplex.com
Off-Chain Storage:
- The JSON URI often points to decentralized storage solutions like IPFS, Arweave or centralized services such as AWS.
- The metadata JSON typically contains fields like:
- name: The token’s name.
- symbol: Its ticker or short identifier.
- uri: A link to additional metadata or assets.
- properties: Custom attributes specific to the token.
Structure Example:
A typical metadata JSON file might look like this:
{
"name": "AlphaArc",
"symbol": "alpha",
"description": "A platform for data-driven blockchain agents. Build your personal AI quant.",
"image": "https://ipfs.io/ipfs/QmcMrfkaERn9jKhCnaFtYRpTMXDn2izrF5aH3prPKoFPxs",
"showName": true,
"createdOn": "https://pump.fun",
"twitter": "https://x.com/AlphaArc4k",
"website": "https://www.alphaarc.xyz/"
}
AlphaArc's Approach to Metadata
- IPFS URL Normalization:
- AlphaArc normalizes IPFS URIs into gateway-compatible URLs, making them accessible for standard HTTP requests.
- Example: hash is extracted from https://ipfs.io/ipfs/QmExampleHash and transformed to ipfs://QmExampleHash
- Metadata Fetching:
- Metadata is not included in chunked datasets by default.
- Instead, AlphaArc provides tools to fetch metadata as a postprocessing step, ensuring the most up-to-date and relevant information.
- Image Optimization:
- Images are resized on demand and CDN cached.
- Error Handling:
- We handle malformed metadata e.g. where the uri just points to a video or image and create synthetic metdata
- We provide error messages as part of metadata to handle different scenarios e.g.
host unreachable
Why Metadata is Not Chunked
Metadata often changes or becomes unavailable if off-chain hosts remove or modify files. Moreover, many tokens have a very short life-time (rug pulls) yet introduce extra data (images, files) bloating the indexing.
By keeping metadata retrieval separate and filtering noise, AlphaArc ensures data integrity and avoids bloating core datasets with potentially stale or incomplete metadata.
Postprocessing Workflow
Clients use AlphaArc tools to:
- Query token mints from the chunked dataset.
- Fetch associated metadata JSON files via normalized URLs.
- Integrate the retrieved metadata into their applications or analyses.
Considerations for Using Metadata
- Dynamic Nature:
- Off-chain metadata can change, so periodic re-fetching may be necessary for applications requiring up-to-date information.
- Performance Impact:
- Fetching metadata in bulk can be resource-intensive, especially for tokens with IPFS-based assets that rely on decentralized networks.
- Recommended Practices:
- Cache fetched metadata locally for frequent reuse.
- Use robust error handling to manage missing or unreachable metadata.
Conclusion
Token metadata on Solana provides valuable context for understanding tokens, but its off-chain nature requires additional processing. AlphaArc simplifies this process by normalizing IPFS URLs and enabling efficient metadata fetching as a postprocessing step. This approach ensures flexibility, up-to-date data, and efficient integration into client workflows without burdening the core datasets.